End-to-End Encryption with AES
Key Generation and Management
- Each user should have a unique encryption key. Use a secure method like RSA to exchange AES keys between
users.
- Use a secure key derivation function like PBKDF2, bcrypt, or Argon2 to derive AES keys from a user
password if necessary.
Message Authentication:
- Use message authentication codes (MACs) or authenticated encryption (like AES-GCM) to verify the integrity
and authenticity of each message.
- Ensure that any tampering with the ciphertext is detectable and results in message rejection.
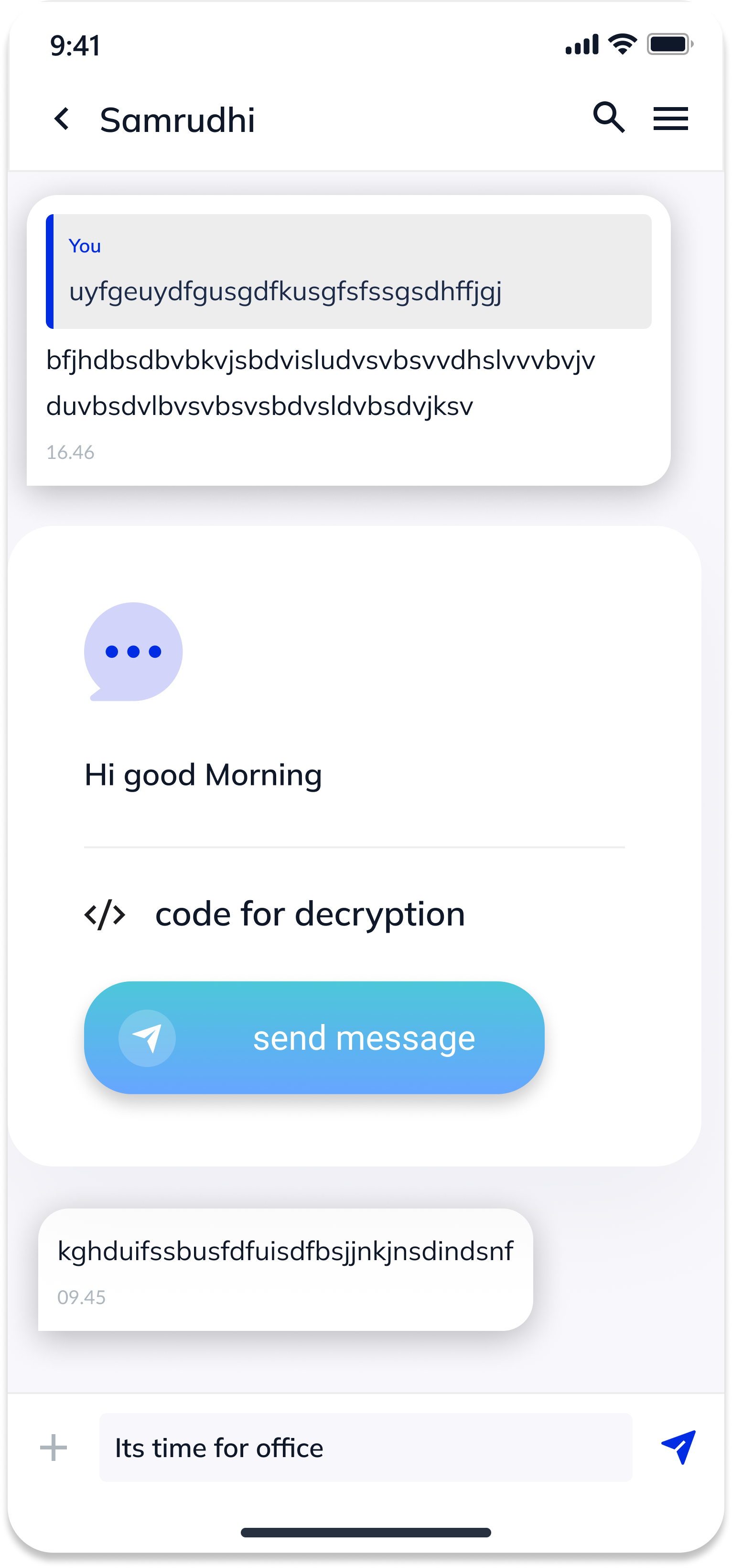
Message Encryption
When a user sends a message, the app should:
- Generate a random IV or VI for the code.
- Encrypt the message using the AES key.
- Send the encrypted message, to the friend.
Message Decryption
Upon receiving a message, the app should:
- Extract the IV or VI and encrypted message.
- Decrypt the message using the IV or VI .
- Display the decrypted message to the user.
Secure Storage
- Store keys and sensitive data in a secure enclave or use OS-level secure storage mechanisms.
- Encrypt any locally stored messages or user data using AES before saving it to disk.
Forward Secrecy
- Implement a mechanism for rotating keys periodically or on a per-message basis.
- Use ephemeral keys for key exchanges to ensure past communications cannot be decrypted even if long-term
keys are compromised.